Today, back pain is the second most common reason for patients seeking medical attention. According to the American National Institutes of Health, one in five middle-aged people suffer from pain. At the same time, the incidence of the disease only increases with age. In medical practice, soreness (dorsalgia) is considered an interdisciplinary pathology, because there is a symptom in the clinic of both neurological and somatic diseases.
At the same time, the incidence of the disease only increases with age. In medical practice, soreness (dorsalgia) is considered an interdisciplinary pathology, because there is a symptom in the clinic of both neurological and somatic diseases.
What is the cause of back pain?
Pain in the back in 90% of cases occurs with diseases of the spine (vertebral pain). In other cases, the cause may be pathologies of internal organs, spinal cord, etc. (non-vertebral pain).
Thus, the vertebrogenic group includes:
- intervertebral hernia;
- sacra- or lumbarization;
- spondylosis;
- osteoporosis;
- tumor processes of the vertebrae;
- trauma (vertebral fractures, spondylolisthesis).
Non-vertebral group includes:
- psychogenic pain;
- fibromyalgia;
- pathology of internal organs (heart attack, pneumothorax, pancreatitis, urolithiasis, etc. );
- tumor formations (neurinomas) and metastases;
- epidural abscess;
- syringomyelia.
Symptoms
The nature of back pain, its strength and duration vary depending on the underlying pathology.
- Intervertebral hernia.A hernial protrusion appears between the vertebrae with the development of osteochondrosis. In this case, the pain can be sharp or aching and be local in nature (depending on the level of the affected disc). Soreness often extends to the limbs, accompanied by numbness and tingling. In advanced cases (when the hernial sac compresses the nerve roots), disorders of the sensitive and motor spheres of the arms or legs may appear. Rarely, there are violations of urination, defecation and sexual function (with damage to the pelvic spine).
- Sacra or lumbarization.Sacralization is a congenital anomaly associated with the fusion of the last lumbar vertebra with the sacrum. In this case, the opposite defect is lumbarization, when the first vertebra of the sacrum is separated and becomes an additional lumbar vertebra. Usually, pathologies are asymptomatic, but the clinic is provoked by excessive physical activity or heavy lifting. In such cases, there is a lumbago pain in the sacrum region, which increases with movement, spreading to the lower extremities. Pathology is also characterized by the fact that it occurs at a young age (usually at 20-25 years old).
- Spondylosis.Spondylosis (unlike the previous ailment) occurs mainly in the elderly. The disease develops as a result of senile changes in the spinal column - its "wear". Pathology is accompanied by the growth of bone tissue in the form of osteophytes, which can lead to complete fusion of the vertebrae. The latter is dangerous with injuries of neurovascular bundles, muscles and surrounding organs. The illness is accompanied by chronic pain that worsens towards the end of the day. Sometimes the pain syndrome manifests itself not only in movement, but also at rest, leading to insomnia. With an uncontrolled disease, there are frequent cases of immobilization of the vertebral joints, as well as pinching of nerve fibers with the development of characteristic neurological disorders.
- Osteoporosis.Osteoporosis is a metabolic disorder, during which the processes of bone destruction prevail over bone formation. The clinical picture of the disease is scanty: usually the pathological process is asymptomatic and is detected by chance (with X-ray). However, in the later stages of the disease, dull pains appear, as well as curvature of posture.
- Tumor processes of the vertebrae.Vertebral tumors are often asymptomatic until they grow large enough to compress nerve fibers. In such cases, chronic back pain (usually in the lower spine) occurs, which can spread to the thighs and lower legs. Sooner or later, tumor growth leads to compression of the nerve roots, which is manifested by neurological disorders: loss of sensitivity and movement in the limbs.
- Injuries.A common cause of acute pain, limited mobility and neurological symptoms are spinal column injuries: fractures, bruises, dislocations / subluxations, as well as "slipping" of the vertebrae due to damage to the ligamentous apparatus - spondylolisthesis. Typically, patients note a sharp diffuse pain in the back, the presence of hemorrhages ("bruising"), local swelling and restriction of movement.
- Psychogenic pain.A similar appearance occurs against the background of complete health after an emotional outburst or stressful situation. Patients describe pain in different ways, which is limited only by the patient's imagination. Sometimes there is a so-called. "Painful behavior" when people, while maintaining mobility, tend to use auxiliary support: crutches, sticks and even wheelchairs.
- Fibromyalgia.The pain syndrome in fibromyalgia is extremely similar to that in psychogenic pain. At the same time, soreness is also provoked by stress, climate and emotional overload. However, an important difference is that the pain should be observed for more than three months, accompanied by local sensitivity at characteristic points (the place of attachment of the occipital muscles, the middle of the trapezius muscles, etc. ). Also, the diagnosis requires the complete exclusion of all kinds of somatic diseases.
- Pathologies of internal organs.Back pain can often appear with diseases of various organs of the body. So, with a heart attack, the pain syndrome is localized behind the sternum, spreading under the scapula and left arm, as well as in the spine. With pneumothorax (accumulation of air under the lining of the lungs), acute chest pain occurs, radiating to the spinal column. A symptom complex arises against the background of difficulty breathing and cyanosis of the face. In pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), the pain syndrome has a different character, arises in the upper abdomen in a "belt" type, covering the sides and back. Back pain appears along with vomiting and indigestion. A complication of urolithiasis is renal colic - an acute paroxysmal pain syndrome. Typically, the pain is so severe that it causes patients to bend over in search of relief. Against the background of an attack, urine turns dirty red due to blood impurities.
- Tumor processes.A neurinoma is a tumor of the nerve sheath. When the roots of the spinal cord are affected, back pain usually occurs, as well as loss of sensitivity and motor activity below the level of the lesion. It is also worth noting that this tumor process is usually benign. However, a similar clinical picture can be caused by metastases of breast cancer, prostate, lung, kidney, etc.
- Epidural abscess.An epidural abscess is a collection of pus under the hard lining of the spinal cord. The disease is accompanied by acute pain syndrome, which is complemented by neurological disorders: paresis (decreased muscle strength), loss of sensitivity, pelvic disorders, etc. often appear. A purulent process occurs against the background of infections, wounds, immunodeficiency or as a complication of lumbar puncture (or epidural anesthesia).
- Syringomyelia.Syringomyelia is a pathology of the nervous system, during which cavities appear in the spinal cord. Injuries, tumors, compression of the brain, etc. provoke the disease. At the initial stages, there is a slight soreness in the spine, which does not bring discomfort. Then there is weight loss, muscle weakness, pain sensitivity is lost, there is no sweating, and the bones become fragile. Often there are injuries to the joints, bone skeleton (burns, fractures, cuts), however, due to the lack of pain sensitivity, they pass unnoticed.
Diagnostics
As a diagnosis, a qualitative survey and physical examination of the patient by palpation (feeling), percussion (percussion) and auscultation (listening) are required. For some pathologies, it is necessary to conduct laboratory blood tests (heart attack, pancreatitis, tumor processes).
To visualize soft tissues and internal organs, you will need instrumental diagnostic methods: ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. Whereas X-ray and computed tomography are used for direct examination of the skeleton.
In some cases, less common techniques may be needed: bone scintigraphy, electromyography, etc.
Back Pain Treatment
To relieve acute back pain, apply ice (for 20 minutes every 4 hours), exclude physical activity, immobilizing the spine if possible. If the pain is unbearable, pain relievers can be taken. However, it is worth remembering that anesthetics "lubricate" the clinic of the disease. Subsequently, this can complicate the diagnosis of the disease. Only the attending physician can prescribe drugs.
Herniated disc
The main drug treatment is based on the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen) and painkillers (Ketorolac). In some cases, surgical removal of the intervertebral hernia may be required, as well as endoprosthetics of the intervertebral disc.
Sacra or lumbarization
When pain occurs, blockades with anesthetics are prescribed, as well as physiotherapy (paraffin applications, electrophoresis, etc. ). With the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, reconstructive operations are indicated.
Spondylosis
Anti-inflammatory drugs (Meloxicam, Indomethacin), as well as physiotherapy (ultrasound, electrophoresis) are used to eliminate inflammation and pain syndrome.
Osteoporosis
Treatment of osteoporosis begins with a diet high in calcium and vitamin D.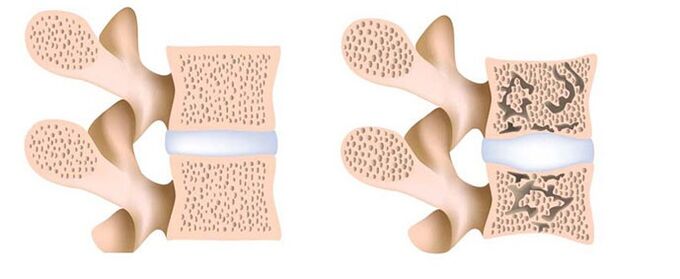 Perhaps the appointment of these substances in the form of drugs. In some cases, hormone therapy with estrogens, calcitonin and parathyroid hormones is used.
Perhaps the appointment of these substances in the form of drugs. In some cases, hormone therapy with estrogens, calcitonin and parathyroid hormones is used.
Tumor processes
Treatment for tumor diseases consists of chemotherapy and surgery. In this case, the amount of assistance depends on the specific clinical case.
Injury
In case of minor injuries, a gentle regimen and warming up are prescribed. In some situations, reduction or skeletal traction is required. When neurological symptoms appear, operations with fixation of bone fragments are performed.
Psychogenic pain
Help with psychogenic pain consists in complex psychotherapy, as well as taking antidepressants (fluoxetine, Sertraline).
Fibromyalgia
Given that the causes of the disease are still unknown, symptomatic therapy is prescribed: antidepressants (Paroxetine, Amitriptyline), anticonvulsants (Pregabalin), hypnotics (Zopiclone) or tranquilizers (Diazepam). Self-attunement for positive thinking, avoiding stressful situations and being in a warm, dry climate are also important.
Pathologies of internal organs
Each of the possible internal pathologies requires individual treatment tactics. Emergency care for a heart attack is taking Nitroglycerin (one tablet every 5 minutes until the ambulance arrives); with pancreatitis - cold, hunger and rest; with pneumothorax - a sealed (occlusive) dressing in the case of an open wound of the lung; with renal colic - antispasmodics (Drotaverinum, Metamizole sodium) and warming up.
Epidural abscess
Treatment consists of urgent surgery to normalize the pressure in the spinal canal and drain the meninges. Antibiotic therapy (Amoxicillin, Cefotaxime) supports surgical intervention.
Syringomyelia
Typically, patients are advised to protect their skin from cuts and burns (the latter often occur because patients lose sensitivity and do not feel trauma). Pain relievers, antidepressants (Fluoxetine), and antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine) are also prescribed. In some cases, surgical intervention is possible in order to revise the formed cavities of the spinal cord.
Back Prevention
For the prevention of back pain, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of each of the pathologies noted above. To do this, you need:

- Normalize lifestyle: reduce body weight to normal; make up a correct diet rich in trace elements and vitamins; ensure proper physical activity without overexertion.
- Give up bad habits: smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Correct posture curvature (scoliosis, lordosis) and orthopedic pathologies (flat feet, clubfoot, etc. ).
- Timely diagnose and treat concomitant diseases of the musculoskeletal system or internal organs.
- Prevent or properly treat spinal column injuries.
- Avoid emotional outbursts and stressful situations.
It is worth remembering that back pain is not an isolated pathology, but a symptom of a disease. The main ailment can be extremely serious and, if untreated, lead to disability and even death of the patient!































