With osteochondrosis of the spinal column, many are familiar not from popular gears from the TV screen, but from their own sad experience.Statistics are harsh: up to 80% of the population suffers from this ailment, which also significantly younger.If earlier complaints about problems in the spine were mainly among the older generation, now children's osteochondrosis is no longer surprising anyone.And the fault of a sedentary lifestyle and the so -called “benefits of civilization”.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is Polietiologic a progressive disease that is manifested by degeneration of the intervertebral discs and dystrophy of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine.Everyone knows about symptoms firsthand, but these knowledge is fragmentary;We will try to structure them, as well as talk about the principles of diagnosis and treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
The causes of osteochondrosis
Medical science cannot unequivocally answer, which is why osteochondrosis occurs.It is reliably known that the sedentary lifestyle that a modern person is prone to negatively affects the progression of this disease.It is interesting that both hypodynamia and colossal loads of athletes lead to proxy of discs.A hereditary factor plays a leading role.The following reasons are distinguished:
- burdened hereditary history;
- obesity;
- hypodynamia;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- traumatic damage to the spinal column;
- long static overloads and work associated with lifting weights (work at the computer, weight lifting, miners, movers, etc.);
- scoliosis;
- dysfunctional environmental situation;
- flat feet and pregnancy;
- hypothermia and stress, which often cause exacerbations of the disease.
There are several neurological syndromes:
- shoulder -shoulder periarthritis;
- root;
- cardiac;
- Vail artery syndrome.
Shoulder -shoulder periarthritis.It is characterized by pain in the neck, shoulder, shoulder joint.The leading neurogenic contracture of the shoulder joint is formed, which is protective in nature, as it protects the axillary nerve from stretching (Antalgic pose).With this position, the muscles surrounding the joint are in tension.The severity of the pain syndrome depends on the degree of exacerbation of osteochondrosis: on a slight limitation of the amplitude of movements in the joint to the so -called “frozen shoulder”, when any movements cause severe pain.The pain intensifies when the shoulder is diverted and pronounced, since it is these movements that enhance the tension of the axillary nerve.
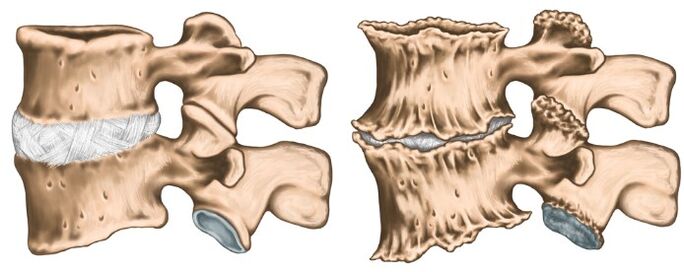
Royshift syndrome (cervical radiculite).Most often occurs with cervical osteochondrosis.At the same time, the spine of the spinal nerve is squeezed due to the “subsidence” of the intervertebral discs, as well as due to the growth of osteofites or protrusion of the discs in the lateral direction.The pain syndrome is specific: intense burning, tearing, pressing pain, which also intensifies when the patient moves his head.Antalgic pose is also noted in the neck muscles, they are sharply tense and painful, the volume of movements is limited.There is pain in the back of the head, neck, front chest, shoulder, between the shoulder blades.Disruption of sensitivity by the type of "half-jacket with short sleeves" is characteristic.
Cardial syndrome.The name of the syndrome is responsible for itself: the clinical picture is very similar to the angina pectoris.In this case, there is no organic damage to the heart, at the height of the pain syndrome, violations of coronary blood flow by ECG are not detected, and such patients are well tolerated.A typical feature with angina pectoris: the pain takes place after taking nitrates, and in the case of osteochondrosis does not change and bothers for a long time.Unlike angina pectoris, the localization of pain is mainly in the heart on the left.With irritation of the roots of segments C8 - T1, rhythm disturbances in the form of tachycardia and extrasystole are possible.This is not due to damage to the conducting system of the heart, but with a violation of the sympathetic innervation of the heart muscle (Extracardiac damage).In the differential diagnosis of angina pectoris and cardiac syndrome, the leading is the fact that, in addition to cardial complaints, the patient notes the increase in pain in the shoulder joint and neck associated with lifting or harsh movements.
Vail artery syndrome.The vertebral artery takes place in a channel formed by holes in the transverse processes of the vertebrae.This artery is paired, it is responsible for the blood supply to the brain.Accordingly, any narrowing of this channel very negatively affects the nutrition of brain tissue.The syndrome of the vertebral artery develops directly both with compression of the artery itself and with irritation of the sympathetic nervous plexus, which is located around it.The pain in this pathology is burning or pulsating in the occipital region with spread to whiskey, tutorial arcs, crows.It arises on both one and on both sides.Patients usually associate aggravation with the condition after sleep in a non -physiological pose, trips in transport, walking.With pronounced symptoms, hearing loss, dizziness, noise in the ears, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, and increasing blood pressure are possible.Such symptoms are not specific and are very similar to complaints in cerebral stroke.This pathology is characterized by the syndrome of the Sistine Chapel: a fainting that occurs when you overturn the head back (severe brain ischemia).He was described by visitors to the Sistine Chapel in the Vatican when they examined the frescoes in her arches.It is also possible to fall without loss of consciousness with sharp turns of the head.
Like any diagnosis in medicine, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis is established on the basis of patient complaints, anamnesis of the disease, clinical examination and auxiliary research methods.X -ray of the cervical spine in direct and lateral projections is performed, if necessary in special positions (with an open mouth).At the same time, experts are interested in the height of the intervertebral discs, the presence of osteofites.Of modern research methods, IAMR and CT research are used, which make it possible to verify the diagnosis most accurately.In addition to the listed methods of additional research, consultations of related specialists (cardiologist, ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon) may be needed, and the examination of the neurologist is simply vital.The neurologist is engaged in the treatment of osteochondrosis, so after examining the patient, he will prescribe the necessary minimum examination at his discretion.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a polyetiological disease, for one course of therapy is not cured.You can’t drink a “magic pill” and everything will pass, it is necessary to fundamentally change your lifestyle, since the trigger is hypodynamia.The most tangible results are easier to achieve in the initial stage of the disease, when the complaints are minimal and there are no compression syndromes and the spinal artery.In the acute stage of the disease, when the following groups of drugs are prescribed pronounced pain: the pain syndrome is pronounced:
- Therapeutic paravertebral blockade (to relieve pain and removal of muscle spasm);
- NSAIDs;
- ointments containing NSAIDs and reflex action;
- muscle relaxants;
- B vitamins V.
As the inflammatory process subsides and the relief of the pain syndrome, they move on to physio-therapy treatment.Most often, the following techniques are used:
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- acupuncture;
- Exercise therapy;
- therapeutic massage;
- Manual therapy.
It is important to understand that osteochondrosis proceeds with periods of exacerbation and remission, therefore it is very important to affect the cause, and not treat the investigation.































